
Fifty percent of the nurses are state registered nurses where 65% of them have had at least 1 year of working experience. Demographic data showed that female nurses make up 55% of the active population age group of 20-40 years (90%) while 45% were male nurses. Of the 75% who identified the causes of infections, 25% noted infections are due to poor aseptic techniques, 20% due to negligence while 5% is due to financial constraints of clients few nurses (45%) use sterile gloves to prevent infection, while 20% use all of the above to prevent the infection and 35% varies ( Figure 1). More than half (75%) of nurses know the causes of infection while 25% don’t identify the causes of infection ( Table 1). Fifty-five percent of the participants indicated that less than 10 wounds get infected, 25% said 10 to 20 wounds get infected while 20% said more than 20 wounds get infected per year than 20 wounds get infected per year. Eighty percent (80%) of the nurses admitted that aseptic techniques are just averagely maintained while 20% strictly follow it. It was observed that, 85% of nurses face problems of wound infection while 15% do not face any problem. Sixty percent of the nurses were married, 35% single and 5% widow.

Ninety-five percent of the nurses were christian while 5% of them were muslim. It was observed that 35% of the nurses had worked for one year or less, while 40% of them had work for 1-5 years and 5-10% of them had work for more than five years. Fifty-Five percent were female and 45% male. Of the nurses, 50% were holders Bachelor of Nursing Science (BNSc), 30% State registered nursing (SRN) and 15% Higher national diploma (HND). A total of 20 nurses were used for the studies. A descriptive analysis on the cases was done.
INFECTION CONTROL AND MEDICAL ASEPSIS SOFTWARE
SPSS version 20.0, statistical software was used in data cleaning, management and analysis. The statistical package Epi Info 7 was used to enter data in this study. Questionnaires that had initially been tested and validated were administered to the participants. Authorization was soughed from the delegate of public health of the North West Region and the director of the Bamenda Regional Hospital to conduct research in his institution. The structured questionnaire had two major sections demographics section and section that investigated the knowledge of the nurses on antiseptic techniques.Įthical approval was obtained from the Institutional Research Ethics Committee for Human Health at the School of Health Sciences of the Catholic University of Central Africa. The instrument used for data collection was a well-structured questionnaire designed according to the objectives. All 20 nurses who constantly came in contact with patients with septic wounds for dressing working at the surgical unit were included in the study. All 20 nurses who constantly came in contact with patients with septic wounds for dressing working at the surgical unit were given informed consent and after approval to participate in the study were administered questionnaires. Our study population were nurses working at the surgical unit.

The study took place at the surgical unit of the Bamenda Regional Hospital, Cameroon. A cross-sectional study was carried out through the administration of a structured questionnaire to healthcare providers (nurses) of the Bamenda Regional Hospital. In Cameroon there is inadequate data regarding nurse’s knowledge, practices and the barriers they faced in the implementation of aseptic techniques thus giving the investigators the motivation to carry out this investigation. Preventing surgical site contamination requires the efforts of all in involved in care of the patient to use their theoretical knowledge and experience in aseptic practices to provide patients with optimal care resulting in positive outcomes. The goal of aseptic technique is to reach asepsis and each healthcare setting has its own principles and guidelines in achieving asepsis.
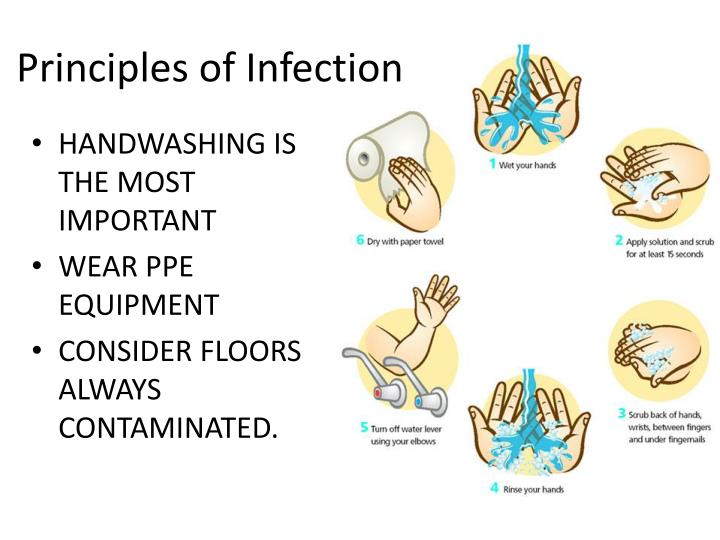
Compliance with these techniques for infection control is important for the safety of patients and personnel’s as this will reduce nosocomial infections in the units and resulting in patients’ shorter stay in the hospital thus a cost reduction in medical aids unlike when there are infections which will results in increased intuitional cost due to a longer stay in hospital admissions. While asepsis applies to both medical and surgical procedures which is the absence of potential pathogenic micro-organisms. To the editors of the Pan African Medical JournalĪseptic technique is the use of practices and procedures such as hand hygiene, non-touch techniques, appropriate aseptic field, sterilized equipments and cleaning existing key parts to minimize the presence of disease causing pathogens.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
